Loops allow us to execute a block of code repeatedly until a certain condition is met with a specific result. This method is useful when we want to run the same code multiple times without having to retype it.
Mojo Supports Two Types of Loops:
- for loop – This type is usable for running a block of code with a fixed number of times for the values.
- while loop – This method is used when your condition becomes true. until it’s not stops the loop.
Loops are important in Mojo and any other programming for:
- Processing data like lists or user input
- Repeating instructions automatically
- Building patterns or logic-based structures
- Controlling program flow based on conditions
1) Processing data like lists or user input: Loops help us to handle multiple pieces of data one by one. For example:
let numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4]
for num in numbers:
print(num * 2) # Process each number
- It processes each number one by one and prints the result of the particular.
- This is useful for lists, files, user input, and databases.
2) Repeating instructions automatically: Loops are also useful if you want to do the same thing multiple times. For example:
for i in range(3):
print("Hello!")
Output:
Hello!
Hello!
Hello!
In this code, we decide the range(3), so it will print “Hello!” three times.
3) Building patterns or logic-based structures: It is help to create logic like checking conditions, building shapes, etc.
Example:
for i in range(5):
print("*" * i)
Output:
*
**
***
****
- This type of example code is also useful for building our programming logic, so if you are a beginner, try this code with multiple logics.
4) Controlling program flow based on conditions: We can also decide how much of the code runs. see the following code:
let count = 1
while count <= 3:
print("Counting:", count)
count += 1
Basic Syntax of for Loop in Mojo:
for variable in range(start, end):
# code block
Example 1: for Loop
for i in range(3):
print("Mojo is powerful!")
Output:
Mojo is powerful!
Mojo is powerful!
Mojo is powerful!
Basic Syntax of while Loop in Mojo:
while condition:
# code block
Example 2: while Loop
let count = 1
while count <= 3:
print("Count:", count)
count += 1
Output:
Count: 1
Count: 2
Count: 3
Count Down Timer Mini Project
It is used as an “Operator” to declare and execute a loop in Mojo.
fn main():
var seconds_left: Int = 5
print("Countdown begins:")
while seconds_left > 0:
print("Time left:", seconds_left, "seconds")
seconds_left = seconds_left - 1
print("Time's up!")
Output:
Countdown begins:
Time left: 5 seconds
Time left: 4 seconds
Time left: 3 seconds
Time left: 2 seconds
Time left: 1 seconds
Time's up!
This code is showing a countdown, and in the code, we have set the count numbers to 5. Whenever it reaches to the final number, it prints the “Time’s up!” message.
How to Control a Loop in Mojo Using break and continue Statements?
We can make loops more powerful with loop control statements. There are two methods used for it:
- break = It is used when you want to exit the loop immediately.
- continue = This statement skips the current iteration and moves to the next operation.
Example – Find First Even Number
fn main():
var numbers = [1, 3, 5, 8, 11, 14]
for num in numbers:
if num % 2 == 0:
print("First even number found:", num)
break
Output:
First even number found: 8
This loop will automatically stop when it finds the first even number. This is helpful for real-time decision-making scripts in projects.
Mini Project: Loop-Based Task Tracker
Let’s create a simple loop-based to-do list project.
Task: Remind students to finish homework 3 times.
fn main():
var reminder_count: Int = 1
while reminder_count <= 3:
print("Reminder", reminder_count, ": Please finish your homework.")
reminder_count = reminder_count + 1
print("No more reminders. Hope your homework is done!")
Output:
Reminder 1 : Please finish your homework.
Reminder 2 : Please finish your homework.
Reminder 3 : Please finish your homework.
No more reminders. Hope your homework is done!
Explanation of this code:
- var reminder_count: Int = 1: Start with reminder number 1.
- while reminder_count <= 3: Keep repeating the reminder until it reaches 3 times.
- reminder_count = reminder_count + 1: It increases the reminder_count by 1 each time
Exercise For Practice
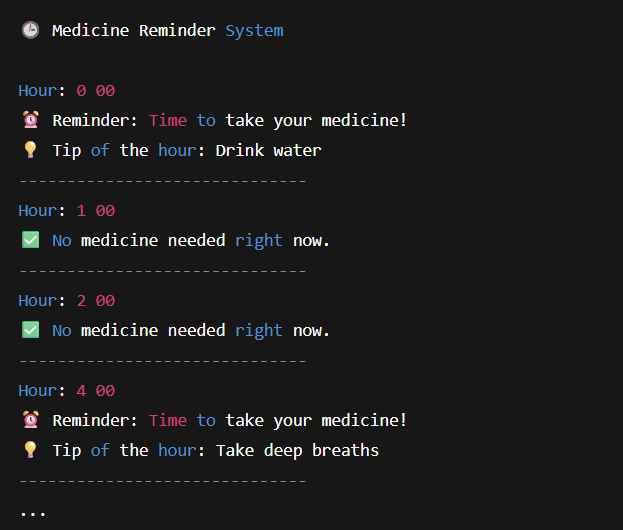
Auto Reminder System for Medicine Timings using Mojo Loops
an auto-reminder system that reminds a patient to take their medicine every 4 hours in a day using Mojo’s for loop.
Create a Mojo program that prints a reminder every 4 hours for 24 hours to take medicine.
The output should indicate like this:
- The hour of the day
- Whether it’s time to take medicine
- A motivational health tip if it’s medicine time
Code Example:
fn main():
var tip_list = ["Drink water", "Take deep breaths", "Stretch your body", "Smile a little!", "Close eyes & relax"]
var tip_index = 0
print("Medicine Reminder System\n")
for hour in range(0, 24):
print("Hour:", hour, "00")
if hour % 4 == 0:
print("Reminder: Time to take your medicine!")
print("Tip of the hour:", tip_list[tip_index])
tip_index += 1
if tip_index >= len(tip_list):
tip_index = 0
else:
print("No medicine needed right now.")
print("-" * 30)
Output of this program: